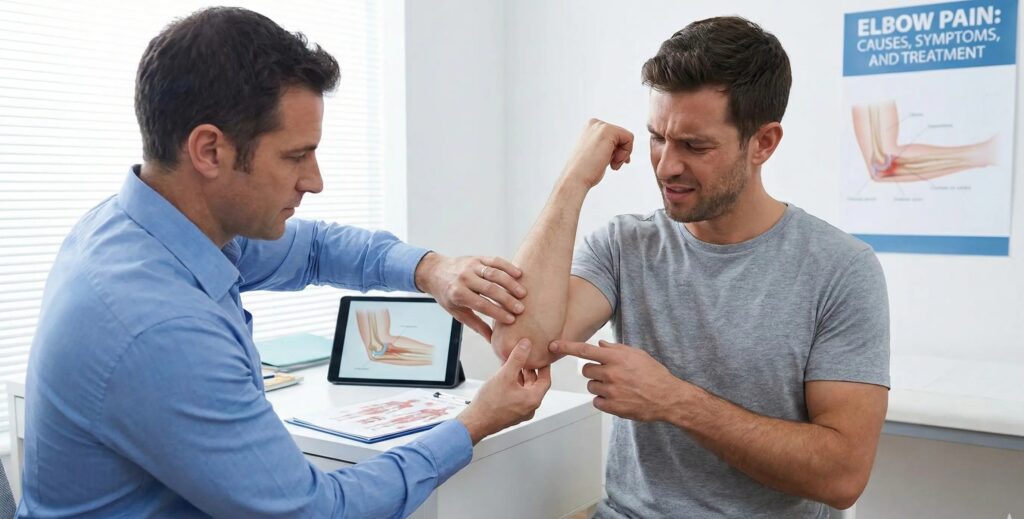
Elbow Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment
Introduction to Elbow Pain
- A frequent condition affecting people at any age is elbow pain. It can be sudden due to an injury, or it can develop over time due to repetitive overuse, poor posture, lifting, throwing, and pushing, or even just ordinary everyday routines, such as opening a door or typing on a keyboard. When the elbow begins to hurt, it can quickly affect work, sports, and even daily activities. Knowing the causes, symptoms, and treatment for elbow pain is important for getting relief and maintaining joint health in the long term. In this blog, we will learn what elbow pain is, what causes it, and the best treatment and prevention methods.
- How it impacts daily life activities – Elbow Pain is a disruption to work, self-care, socialization, writing, hobbies, and even sleep, which leads to increasing levels of frustration, anxiety, and mood shifts. When the joint is stiff, swollen, or weak—even simple tasks become difficult to perform or nearly impossible to complete.
What is Elbow Pain?
- A general discussion of the elbow joint— The elbow is a hinge joint that connects the upper arm bone (the humerus) with the two forearm bones (radius and ulna). Support comes from bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments, nerves & blood vessels. Due to the strength and flexibility of the elbow, it creates motion, which allows the arm to be straightened and bent and the forearm to be rotated.
Classification of elbow pain (acute vs chronic)—Elbow pain is considered acute if it occurs suddenly, such as from a fracture or sprain; chronic elbow pain is long-term, lasting more than three months, and results from repeating a movement or activity that stressed the elbow.
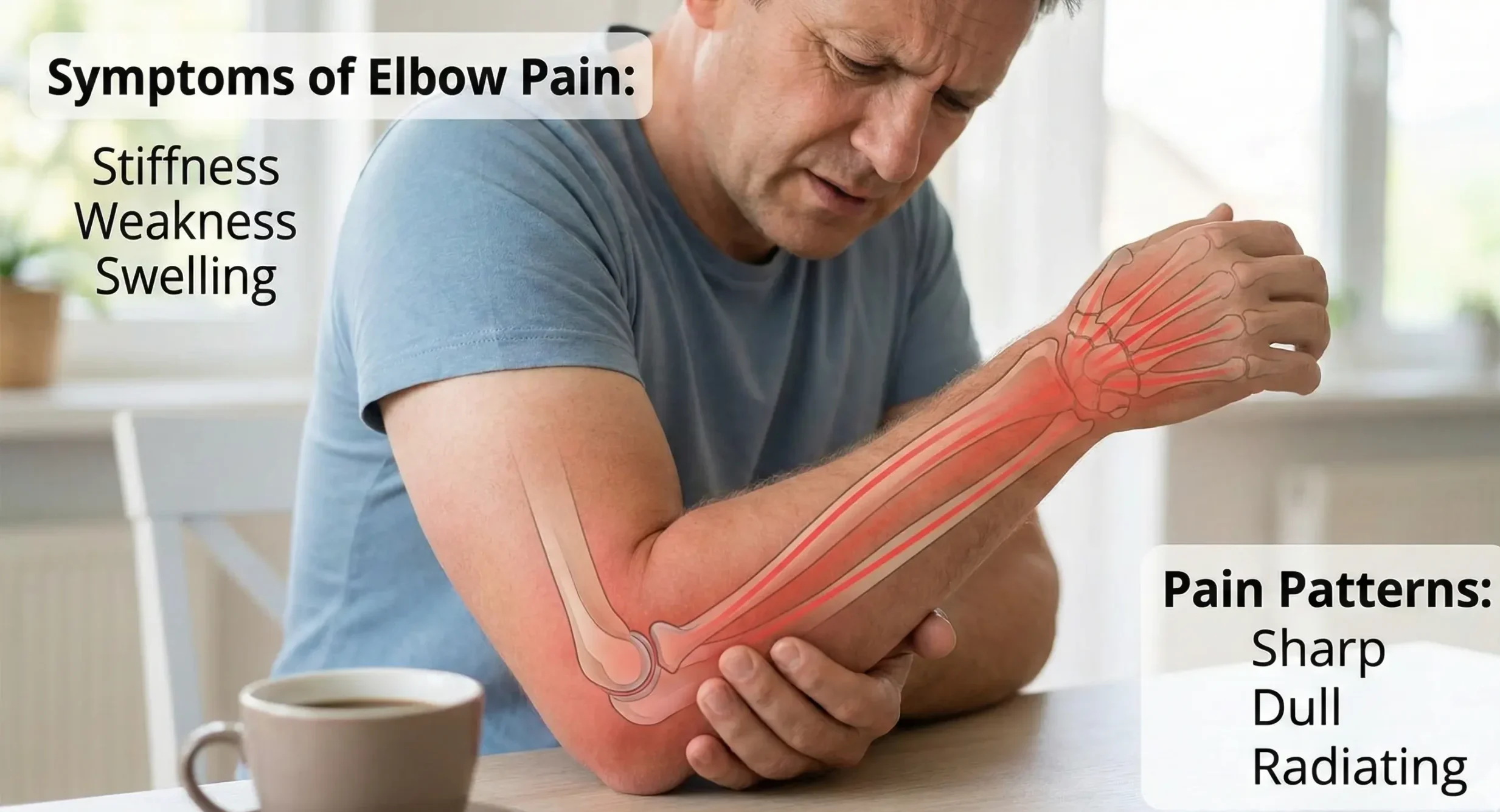
Symptoms of Elbow Pain
- Common symptoms (weakness, swelling, stiffness) — Elbow pain can cause a number of symptoms, such as stiffness, weakness, and swelling, which affect everyday activities such as lifting, gripping, or bending the arm. You may also notice that your elbow feels swollen, tender, or warm, especially if you have sustained an injury or if there is some inflammation. Stiffness may hinder you from fully bending the elbow or straightening it. Weakness results in less grip strength and less stability of the arm. Pain usually increases with any type of movement that involves twisting the arm or extending the arm.
- Pain Patterns (sharp, dull, radiating) -Sharp Pain—is abrupt, unbearable pain that is commonly associated with an acute injury.The sharp pain may start due to any rapid movements or objects being lifted or shifted.Dull Ache—the mild to moderate pain that can relate to overuse, arthritis, and stress on the joint/chronic issues.Radiating Pain—pain that is referred, or spreads from the elbow into the forearm, wrist, or fingers, related to nerve irritation in most cases.

Causes of Elbow Pain
- Injuries (sprains, fractures, dislocations)
- Sprains and strains: From overstretching or tearing ligaments/tendons.
- Fractures: Broken bones in or around the elbow joint.
- Dislocations: When the bones of the elbow are forced out of place.
- Overuse conditions (tennis elbow, golfer’s elbow) –
- Tennis Elbow—Pain on the outer elbow due to repetitive wrist extension (e.g., racquet sports, typing).
- Golfer’s Elbow—Pain on the inner elbow from repetitive wrist flexion (e.g., lifting, ripping).
- Arthritis and joint degeneration—Osteoarthritis: Wear-and-tear damage causing stiffness and pain.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Autoimmune inflammation that can affect the elbow joint.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa (fluid-filled sac) leading to swelling and tenderness.
- Arthritis and joint degeneration—Osteoarthritis: Wear-and-tear damage causing stiffness and pain.
- Repetitive Strain & Compression
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome: Compression of the ulnar nerve (inner elbow), causing tingling or numbness in the ring and little fingers.
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome: Compression of the radial nerve (outer elbow), leading to aching pain and weakness.
Diagnosis of Elbow Pain
- Physical examination—Checking for swelling, tenderness, range of motion, grip strength, and pain during specific movements; identify the exact point of pain.
- Medical history—if past accidental injuries happened.
- Get medical assistance—consult a doctor or physiotherapist.
- Diagnosis test if needed—to detect the location of pain.
- X-rays (detect fractures, dislocations & arthritis.)
- MRI for ligament issues, tendon, or nerve problems.
- CT scan: (Used for complex injuries for a detailed view.)
- Blood or nerve tests (if needed)—check for nerve compression & infection
Treatment Options for Elbow Pain
- Home remedies & self-care: rest, medications, ice & heat therapy, yoga & exercise, short breaks & posture correction; avoid repetitive movements that aggravate the pain.
- Medications—pain relievers, topical creams, or gels . For severe cases, a doctor may prescribe surgery or injections.
- Ice & heat therapy helps to reduce swelling & pain. Warm compresses stiffness and helps in blood flow. Cure diseases like arthritis.
- Physiotherapy & strengthening exercises—Consult a physiotherapist, who may guide perfect stretching & strengthening exercises to relieve stiffness.
- Bracing & support—Braces or elbow straps help reduce stress on tendons, especially in tennis elbow or golfer’s elbow, and also help in nerve compression.
- Injections (steroids, platelet-rich plasma)—For severe cases and accidental damage, use injections prescribed by professionals.
- Surgical treatments—If pain does not improve with conservative treatments, surgery may be considered. This includes surgeries like arthroscopy, ligament repair , tendon , joint replacement surgery .

Elbow Pain in Different Groups
- Athletes and sports-related injuries – Athletes experience elbow pain due to repetitive strain and overuse. This includes – Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis) , Golfer’s elbow , ligament sprains and tendon injuries
- Office workers and repetitive strain -Modern desk jobs may seem low-impact, but repetitive micro-movements and Those who spend long hours typing, using a mouse, or performing repetitive desk tasks often develop strain-related elbow pain.
- Older adults and degenerative conditions – Elbow pain in seniors often stems from chronic degeneration and past trauma . With age, natural wear and tear of the joints can lead to elbow pain . this includes diseses like Osteoarthritis , Rheumatoid arthritis, Reduced muscle strength.
When to See a Doctor Urgently
- Sudden swelling or pain – If your elbow pain is associated with swelling, warmth, or redness, it may signal a serious injury such as a fracture, dislocation, or an infection in the joint.
- Inability to move the elbow – Loss of motion due to pain, stiffness, or blockage—may point to a dislocation, joint effusion, or nerve compression. If you cannot bend or straighten your elbow, or if movement causes sharp pain, medical evaluation is essential.
- suspected fracture – Any obvious deformity, misalignment, or bone protrusion requires emergency medical care. Fractures or dislocations need immediate attention to ensure proper healing and to avoid long-term joint issues.

Conclusion
- Elbow pain is a common problem that can affect anyone—from athletes and office workers to older adults.Elbow pain may seem minor at first, but it can quickly escalate if ignored. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is key to managing pain effectively and preventing long-term complications.
- Key takeaways – Don’t ignore severe or sudden elbow pain. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications, restore mobility, and reduce long-term discomfort.Elbow pain has many faces thus Early prevention is necessary to reduce risk. At early stage and after prevention Relief strategies like ice therapy, stretching, excercise , physiotherapy are affectable .
- Importance of timely treatment and prevention – Delaying care can lead to chronic pain, reduced mobility, or even permanent joint damage. Timely diagnosis allows for targeted treatment, preventing complications and speeding up recovery. Preventive measures—such as proper technique in sports, ergonomic adjustments at work, and regular exercise—can minimize the risk of recurrence and keep your elbows strong and pain-free.
- Elbow pain should not be ignored, as early diagnosis and targeted physiotherapy help restore strength and mobility, reduce the risk of long-term joint damage, and provide effective prevention and treatment through expert care available at Phoenix Physio
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes elbow pain?
Elbow pain can come from overuse (repetitive strain), tendon irritation like tennis or golfer’s elbow, trauma (sprains, fractures), bursitis, nerve compression, arthritis, and referred pain from the shoulder or neck.
What are the common symptoms of elbow pain?
Symptoms include pain or tenderness around the joint, swelling, stiffness, reduced range of motion, weakness in grip, and sometimes numbness or tingling from nerve involvement
How do I know if my elbow pain needs physiotherapy?
If pain persists after a few days of self-care, limits daily activities, recurs with movement, or is associated with weakness or swelling, a physio assessment is recommended to diagnose and treat the underlying cause.
What will a physiotherapist do for my elbow pain?
Assessment includes history, joint and soft-tissue examination, and sometimes referral for imaging. Treatment is tailored and may include manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, mobilisation, taping/bracing, and pain-modulating modalities.
What's the best treatment for elbow pain?
Elbow pain, often from overuse like tennis elbow, is treated with rest, ice, anti-inflammatory meds (ibuprofen, naproxen), and braces (RICE method), but professional help involves physical therapy (strengthening, stretching), steroid injections, PRP, or rarely surgery, focusing on reducing pain, inflammation, and restoring function through rest and targeted exercises.